Gene Expression
November 10Papers to discuss:
Vasemagi and Primmer 2005.pdf
Challanges for identifying funtionally important genetic variation: the promise of combining complementary research strategies
Molecular Ecology (2005) 14, 3623-3642
michel et al 2004.pdf
Somatic mutation-mediated evolution of herbicide resistance in the nonindigenous invasive plant hydrilla (Hydrilla verticillata) by Michel et al. Molecular Ecology 13:3229-3237.
Brain and Gonadal Aromatase as Potential Targets of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in a Model Species, the Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Sequence polymorphism can produce serious artefacts in real-time PCR assays: hard lessons from Pacific oysters.
BMC Genomics. 2008 May 20;9:234.
Evaluation of the Branched-Chain DNA Assay for Measurement of RNA in Formalin-Fixed Tissues
Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, Vol.10, No.2, March 2008
Website about use of zebrafish as a research model.

Technology for creating zebrafish knockouts
Learn more about endocrine disruptors
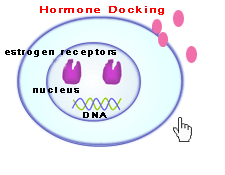 |
| Estrogen Receptor Binding |

QuantiGene® Reagent System----
QuantiGene® Reagent System


- [[http://www.panomics.com/index.php?id=product_3&q=quantigene reagent system#product_overview_3|Overview]]
- [[http://www.panomics.com/index.php?id=product_3&q=quantigene reagent system#product_works_3|How it Works]]
- [[http://www.panomics.com/index.php?id=product_3&q=quantigene reagent system#product_lit_3|Literature/Support]]
- [[http://www.panomics.com/index.php?id=product_3&q=quantigene reagent system#catalog_listings|Catalog Listings]]
- Quantitatively measure gene expression with unparalleled accuracy and precision
- RNA quantitation directly from cultured cell lysates or tissue homogenates
- No RNA purification
- No reverse transcription
- No target amplification
- Simple assay workflow
- Widely used in biomarker discovery, secondary screening, microarray validation, quantification of RNAi knockdowns and predictive toxicology
Principle of QuantiGene Assay
Principle of QuantiGene Assay
| Step 1 Lyse cells to release mRNA in the presence of target probes. Target mRNA from lysed cells is captured by hybridization and transferred to the Capture Plate. |
 |
| Step 2 Signal amplification is performed by hybridization of the bDNA Amplifier and Label Probe. |
 |
| Step 3 Addition of chemiluminescence substrate yields a luminescent signal that is proportional to the amount of mRNA present in the sample. |
 |
Hydrilla in Washington
Click on the presentation below for hydrilla info in Florida
Schardt_%20Jeff.pdf

Other approaches for characterizing gene expression:
*Additional Papers on the topic:
Evaluation of DNA microarray results with quantitative gene expression platforms
Nature Biotechnology Vol. 24, No. 9, September 2006
Trant et al.pdf
Developmental expression of cytochrome P450 aromatase genes (CYP19a and CYP19b) in zebrafish fry (Danio rerio)
Journal of Experimental Zoology 290:475-483.
EHP114pa700PDF.PDF
An easy read about biomarkers and environmental health